Best Treatment In Peripheral Neuropathy
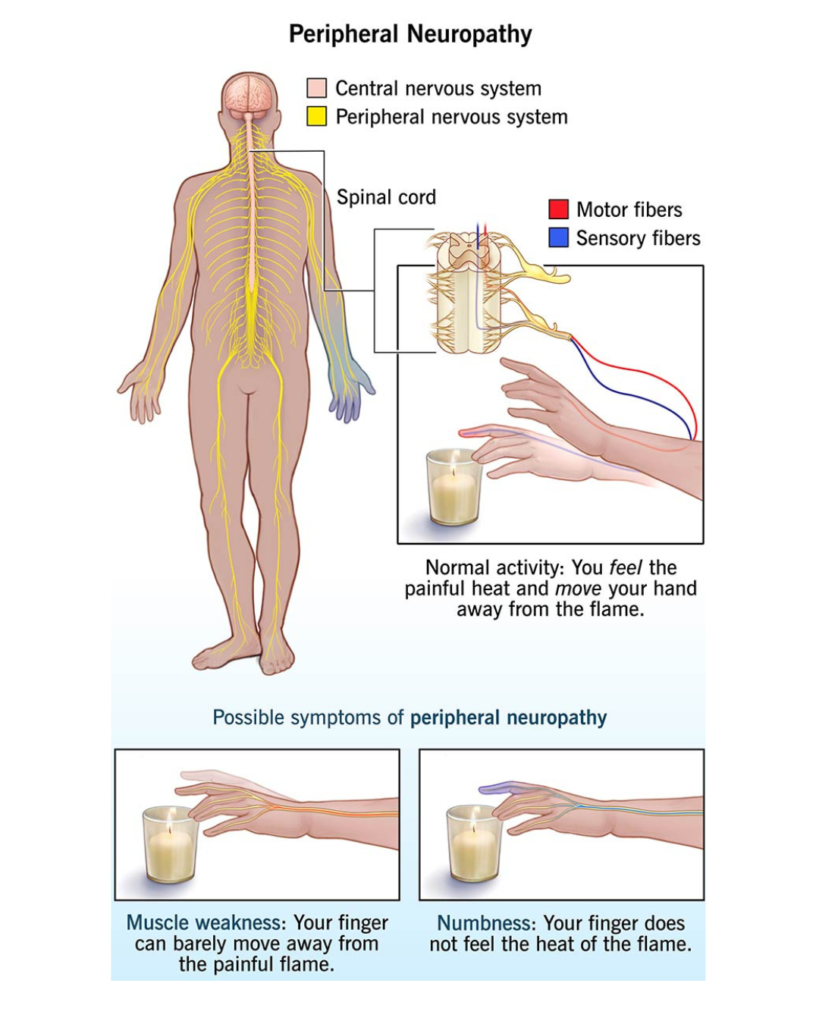
Peripheral Neuropathy (PN) is a collective term describing disorders of the peripheral nerves—the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves include motor nerves, sensory nerves, and autonomic nerves. Damage to any of these nerves leads to symptoms such as weakness, numbness, burning pain, tingling, or loss of sensation, especially in the hands and feet.
Peripheral neuropathy is not a single disease; it is a manifestation of many underlying conditions. It may result from diabetes, injuries, infections, nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune diseases, toxins, or hereditary disorders. Because the peripheral nervous system controls movement, sensation, and autonomic functions, neuropathy can affect many aspects of life.
Below is a detailed explanation of its definition, types, causes, symptoms, pathophysiology, diagnosis, complications, and management.
1. INTRODUCTION AND DEFINITION
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves. The word “neuropathy” means nerve disease (“neuro” = nerve, “pathy” = disease). Peripheral nerves behave like communication cables that send signals from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body and bring sensory information back.
When these nerves are damaged, signals become:
- Weak
- Distorted
- Interrupted
- Overactive
- Absent
This results in sensory loss, motor weakness, or autonomic dysfunction.
2. ANATOMY OF PERIPHERAL NERVES
Peripheral nerves are categorized into:
A. Motor Nerves
Responsible for movement:
- Walking
- Lifting
- Hand grip
- Reflexes
Damage causes weakness or muscle wasting.
B. Sensory Nerves
Responsible for:
- Touch
- Pain
- Temperature
- Vibration
- Position sense
Damage causes numbness, tingling, burning, or loss of sensation.
C. Autonomic Nerves
Control involuntary functions:
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Digestion
- Bladder and bowel function
- Sweating
Damage causes abnormal sweating, digestive issues, or blood pressure changes.
Peripheral neuropathy can affect any combination of these nerves.
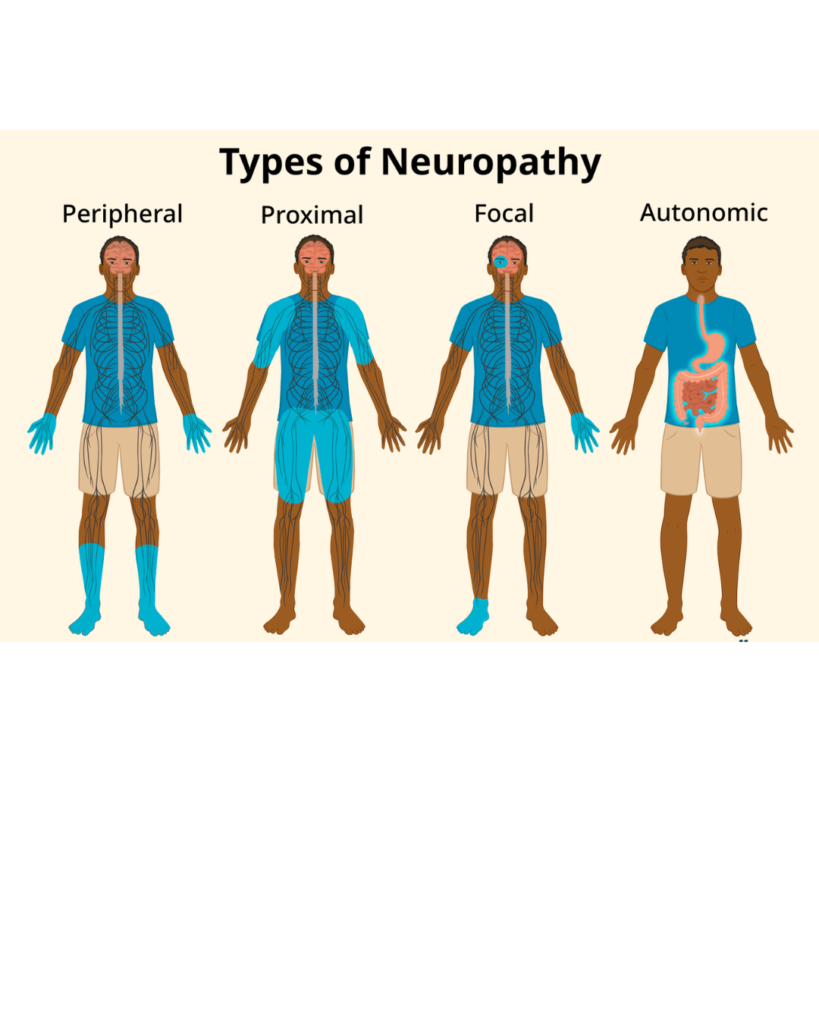
3. TYPES OF PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Based on nerves involved:
1. Sensory Neuropathy
Most common. Symptoms include:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Burning pain
- Loss of vibration sense
- Difficulty feeling feet while walking
2. Motor Neuropathy
Affects muscles:
- Weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Wasting
- Difficulty lifting objects
- Foot drop
3. Autonomic Neuropathy
Affects internal organs:
- Irregular heartbeat
- Excessive or reduced sweating
- Dizziness
- Bladder problems
- Constipation or diarrhea
4. Mixed Neuropathy
Most patients have involvement of all three nerve types.
Polyneuropathy
Damage to multiple nerves → common in diabetes, alcoholism, infections, etc. This is the most typical form of peripheral neuropathy.
1️⃣ Based on the Type of Nerve Fibers Affected
1. Sensory Neuropathy
Affects nerves responsible for sensation.
Symptoms:
- Tingling
- Burning
- Numbness
- Loss of vibration sense
- Difficulty in feeling pain or temperature
Common in: Diabetes, vitamin deficiency.
2. Motor Neuropathy
Affects nerves that control movement.
Symptoms:
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Twitching
- Foot drop
- Difficulty in walking
Common in: Guillain-Barré Syndrome, Charcot-Marie-Tooth.
3. Autonomic Neuropathy
Affects involuntary functions.
Symptoms:
- Blood pressure fluctuations
- Abnormal sweating
- Digestive problems
- Bladder dysfunction
- Sexual dysfunction
Common in: Diabetes, alcoholism.
4. Mixed Neuropathy
Combination of motor + sensory + autonomic involvement.
Most common type.
Seen in: Diabetes, autoimmune diseases.

Leave a Reply